WBS in the Age of Agile
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is often associated with traditional project management methodologies such as Waterfall. In the age of Agile Project management, has the WBS tool lost its edge? Let's find out.
What is a WBS?
Work breakdown structure (WBS) is a critical tool in the Project management toolbox for planning, monitoring, and control of a project. WBS also plays an important role in planning the schedule, resources and cost of a project.The WBS concept was described by NASA and the US Department of Defense (DOD) in 1962. In the age of Agile Project management, has the WBS tool lost its edge? Before we look into that, let’s first refresh our understanding of WBS.
The project management institute (PMI®) defines WBS as follows: “A WBS is a hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables.”
A WBS is a tree structure of different tasks and deliverables that need to be done to complete a project. While the Project Goal defines the Why of the project, the WBS tells the What of the project. It is important to note that a WBS created in a tree format is more easy to read and understand, than a WBS created in a list format. Hence it is highly recommended that a WBS be created in a tree format, either in an online whiteboard (like Miro or Mural) or can also be created using sticky notes on a physical whiteboard. WBS can be created in various forms and there is no wrong or right way, till you are able to meet the objective of creating a WBS, which is to break down the work into meaningful chunks.
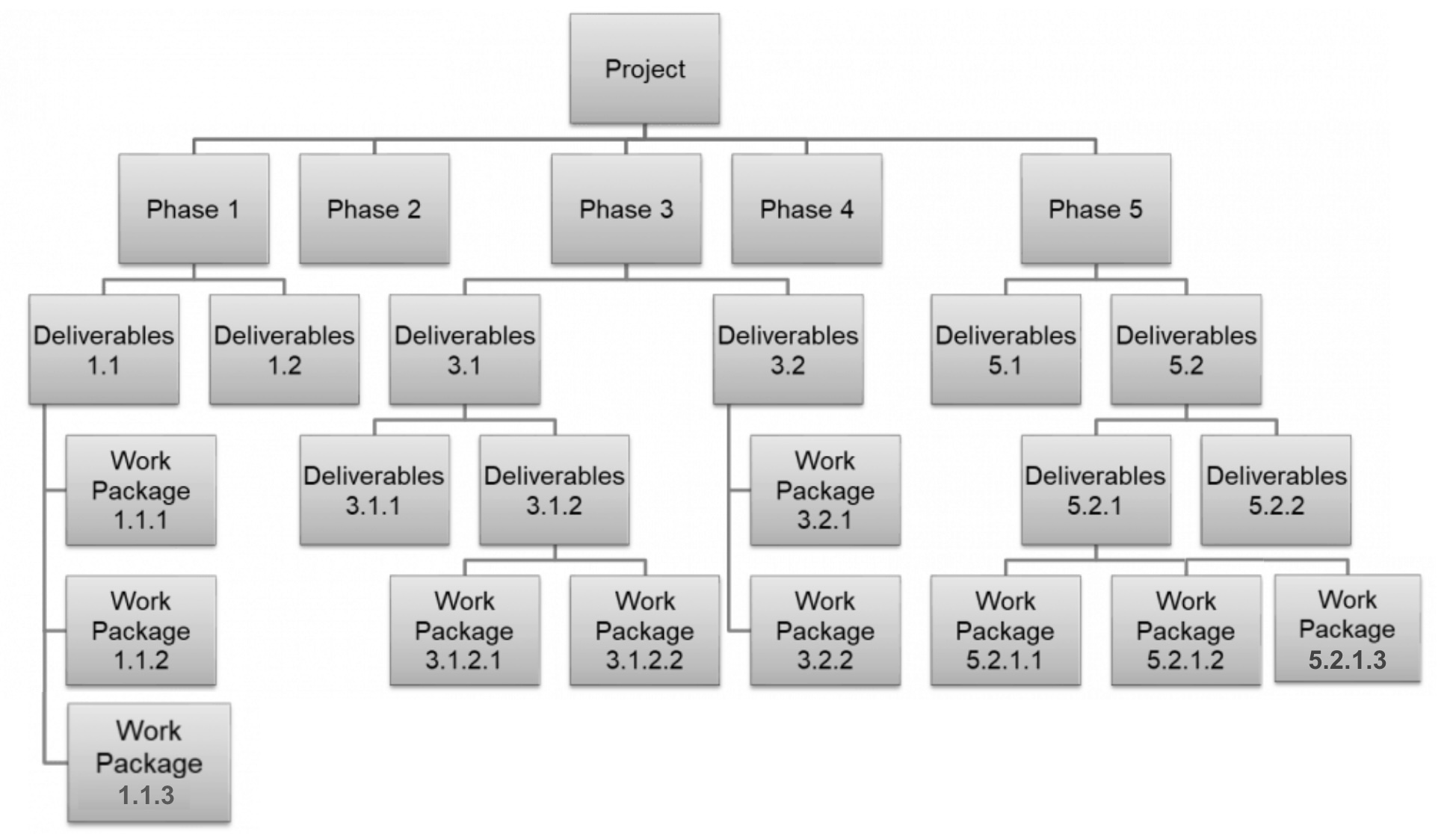
Advantages of using a WBS
- Understanding the Scope better: Many times project teams have a high level scope statement and then directly jump into creating work packages and start executing them. And on a project with tight deadlines and steep requirements, missing something out can affect the outcome of the project. The exercise of creating a WBS can help you identify all the elements and generate a comprehensive project scope. You’ll avoid missing individual tasks or deliverables that might have been otherwise overlooked.
- Improves collaboration and communication: WBS is a collaborative effort and when the teams get together to brainstorm on the WBS, they are more involved in the project planning and defining the work packages. The roles of the teams are better understood and the teams get an opportunity to collaborate more effectively, which has a positive impact on the long term success of the project.
- Minimises changes and helps identify Scope creeps: As the project goals and objectives are well understood and captured in the WBS, it means that fewer changes are required during the execution of the project. Moreover any scope creeps can be more easily identified and managed.
- Helps to identify Risks: When teams collaborate for brainstorming the work packages of the WBS - technical risks, scheduling risks, resource risks can be more easily identified. A WBS discussion aids in identifying risks and also in creating risk mitigation strategies.
- Assists in scheduling, resource requirements and labour cost estimation: WBS is a critical input for creating a project schedule. Typically a Gantt chart view is created to depict the project schedule where the WBS tree view is converted into a list view and start dates, end dates and dependencies are identified. WBS also assists in identifying the resource needs of each work package thus ensuring that the right resources are engaged on the project and it also helps in calculating the resource cost for the project.
WBS best practices
- 100% Rule: This is the most important work management principle to construct a WBS. It consists of including 100% of the work defined by the project scope, which is divided into WBS levels that contain project deliverables, work packages and tasks. This rule applies to all the levels of the WBS, so the sum of the work at a lower WBS level must equal the 100% of the work represented by the WBS level above without exception.
- Keep Tasks Mutually Exclusive: This simply means that there’s no reason to break out individual tasks for work that is already part of another task. If the work is covered in a task because it goes together with that task, then you don’t need to make it a separate task.
- Go Just Deep Enough: You can get crazy with subtasks on your WBS. The WBS has to be detailed, but not so deep that it becomes confusing. Ideally, think maybe three or five at most levels.
- Collaborative effort: Engage your project core team and have a working session with them to create an effective WBS. It also helps to create ownership and accountability.
- Used throughout the project: During the planning phase the WBS is used for creating the Gantt chart schedule. But WBS can be used throughout the project to identify Scope creeps. If an activity identified during execution is not on the WBS, it is most likely a scope creep and should be logged as a Scope change.
- Bottom up planning tool: WBS can also help to create the high level schedule of the project.
WBS in the age of Agile & Hybrid project management
WBS is often associated with traditional project management methodologies such as Waterfall, where tasks are interdependent and goals are not expected to change. Because WBS is suited to this predictive framework, some believe that it is not flexible enough to match the Agile mindset.
However this is a myth, WBS can also be a highly useful tool for Agile or Hybrid projects. In Agile projects, Project Managers can use a work breakdown structure to simplify large epics, breaking them down into smaller units: themes, stories, and tasks. These user stories are often connected via the process of story mapping, which forms a hierarchy and helps to create a holistic view of the project. This is complementary to the hierarchy of the WBS, which can be tailored to suit an Agile project.
In hybrid projects, like the ones we manage in Zalando, we can use a phase-oriented WBS for overall project management, with an activity-oriented WBS for specific tasks or deliverables. More and more software development companies today adopt a hybrid approach to take advantage of the planning rigour of Waterfall with the flexibility of Agile.
Managing projects via Agile or Hybrid methodologies doesn't mean that you cannot adopt the best practices of project planning, which includes the use of a WBS.
Have you created a WBS for your project?
If you have any good examples of WBS that you have created for your project, do share a link in the comments section below. If you have not used a WBS on your project yet, I strongly advocate the use of a WBS in your next project and I assure you that it will have a positive impact on the outcome of your project.
References



